
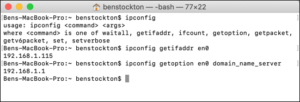
Using a Linux-based operating system, DNS servers are managed using the dns command. Nslookup displays the results when it is not interactive with the DNS server.
Dns Search Linux: Interactive And Non-interactive Modesĭuring the lookup process, you are asked for input at every step. A CNAME (canonical name) record can also be seen if you enter -t (type) SOA. This command can be used to focus on SOA (start of authority) records. The host command has so many options that it may take some time to get used to them. You must also include additional information such as a host name, an IP address, or a domain name. With the Domain Name System (DNS), it can access a variety of information. In addition to retrieving a large amount of useful information from the domain name service, the host command can also query other websites. This will let you search for DNS information using the Linux host command. It is useful for troubleshooting DNS issues, but it also displays DNS information. This service, known as Domain Information Groper, collects data about domain names. The Linux dig command is used to collect information about the DNS. In this video tutorial, we will walk you through how to find your DNS server’s IP address on an IP router or dhcp server running Linux or Unix. In addition, use the dig and host commands to test the validity of DNS. Using the cat command, you can determine a computer’s DNS or IP address. There’s a file called /etc/nf in the /etc/resolv directory in Linux, UNIX, Mac OS X/MacOS, and MS-Windows.

Most Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use caching DNS servers to reduce network load. The DNS servers of the Internet play an important role in the flow of data. How Do I Find My Dns In Terminal?īy typing /displaydns, you can see your current DNS settings.ĭNS is a name given to a computer system used to designate a domain name. It can be used in batch files to automate DNS management tasks when using scripts. The contents of /etc/resolv are a good way to determine which DNS servers are being used. A dig command can be used to troubleshoot DNS issues. The host command is a tool that allows you to perform DNS lookups.ĭNS information is gathered using the Linux dns dig command. Finally, you can also use the ‘host’ command to check DNS in Linux terminal. Nslookup is a tool that allows you to query DNS servers for information about hostnames, IP addresses, MX records, and so on.

Another way to check DNS in Linux terminal is to use the ‘nslookup’ command. Dig is a tool that allows you to query DNS servers for information about hostnames, IP addresses, MX records, and so on. If you want to check DNS in Linux terminal, there are several ways to do it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
